Glycerin
What is Glycerin?
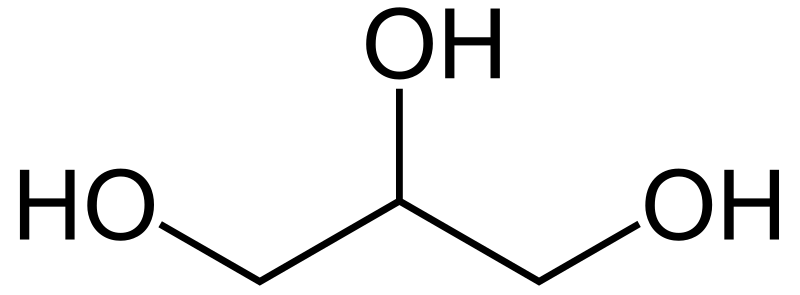
Glycerin, also known as glycerol or glycerine, is a colorless, odorless, and sweet-tasting chemical compound. It is a trihydric alcohol, meaning it contains three hydroxyl groups (-OH) in its molecule. Glycerin is both naturally occurring and synthetically produced and has a wide range of applications in various industries due to its unique properties.
Applications of Glycerin
- Pharmaceuticals: Glycerin is used in the pharmaceutical industry for its hygroscopic (water-attracting) properties. It is a common ingredient in cough syrups, suppositories, and topical medications, where it serves as a moisturizing and emollient agent.
- Food and Beverage: Glycerin is used in the food industry as a sweetener, humectant, and solvent. It is often found in baked goods, dairy products, and confectionery items. In beverages, it can improve the texture and mouthfeel of certain drinks.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: Glycerin is a key ingredient in skincare and personal care products, including lotions, creams, soaps, and shampoos. It helps retain moisture, providing hydration to the skin and hair.
- Pharmaceuticals: Glycerin is used in the pharmaceutical industry for its hygroscopic (water-attracting) properties. It is a common ingredient in cough syrups, suppositories, and topical medications, where it serves as a moisturizing and emollient agent.
- Food and Beverage: Glycerin is used in the food industry as a sweetener, humectant, and solvent. It is often found in baked goods, dairy products, and confectionery items. In beverages, it can improve the texture and mouthfeel of certain drinks.
- Chemical Industry: Glycerin serves as a feedstock for the production of various chemicals, including nitroglycerin, which is used in explosives, and propylene glycol, which has numerous industrial applications.
Glycerin: Benefits
The utility of glycerin can be attributed to several key advantages:
- Hydration: Glycerin’s ability to attract and retain water makes it an effective moisturizer for the skin and hair. It helps combat dryness and promotes softness.
- Solvent: Glycerin is an excellent solvent for many substances, making it valuable in various formulations, including cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food products.
- Safe and Non-Toxic: Glycerin is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies, and it is well-tolerated by most individuals.
- Versatility: Its versatility in various applications, from food and pharmaceuticals to personal care and chemical processes, underscores its importance in modern industries.
How Glycerin is Made
Glycerin can be produced through various methods, but the most common is the hydrolysis of fats and oils. The process involves the following steps:
- Hydrolysis: Fats or oils, which are triglycerides, are hydrolyzed (broken down) using water and a catalyst, typically an alkali like sodium hydroxide or an enzyme.
- Neutralization: After hydrolysis, the mixture is neutralized to remove excess alkali, resulting in a mixture of glycerin and soap.
- Separation: The glycerin is separated from the soap through a process called saponification, which yields crude glycerin.
- Purification: Crude glycerin undergoes purification processes to remove impurities, resulting in the high-purity glycerin used in various industries.
In conclusion, glycerin is a versatile compound with numerous applications in pharmaceuticals, food, cosmetics, and various industrial processes. Its hydrating properties, safety, and versatility make it a valuable ingredient in a wide range of products, supporting health, beauty, and various industrial processes. Understanding the benefits and production process of glycerin underscores its significance in modern life and industry.
Where can I buy Glycerin in Europe ?
Contact us for Glycerin availability and prices