EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid)
What is EDTA?
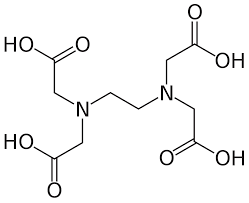
Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid, commonly known as EDTA, is a versatile chemical compound with a wide range of applications across various industries. This synthetic organic compound is highly valued for its chelating properties, which allow it to form stable complexes with metal ions. This property makes EDTA an essential chemical in industries where controlling and removing metal ions is critical.
Applications of EDTA
- Water Treatment: EDTA is widely used in water treatment processes. It serves as a chelating agent to control and remove metal ions like calcium and magnesium, which can lead to scaling and reduce the efficiency of water treatment equipment.
- Detergents: In the detergent industry, EDTA is a key ingredient, especially in heavy-duty and industrial cleaning products. Its chelating properties help improve the detergency of these products by binding to metal ions that can interfere with cleaning agents.
- Food Preservation: EDTA is used in the food industry as a preservative to maintain the quality and shelf life of various food products. It can prevent the oxidation of certain vitamins and the deterioration of color, flavor, and texture.
- Medicine and Pharmaceuticals: EDTA is employed in medicine and pharmaceuticals for various purposes, including as a chelating agent to treat heavy metal poisoning and as a stabilizer for certain medications.
- Agriculture: In agriculture, EDTA is used as a chelating agent in micronutrient fertilizers. It helps improve the availability of essential metal ions like iron, zinc, and manganese to plants, promoting healthier growth.
EDTA: Benefits
The use of EDTA offers several key benefits:
- Effective Chelation: EDTA’s ability to form stable complexes with metal ions makes it highly effective in controlling the presence of these ions in various processes.
- Improved Cleaning: In detergents, EDTA enhances cleaning efficiency by sequestering metal ions that can interfere with cleaning agents’ performance.
- Water Quality: In water treatment, EDTA helps maintain water quality by preventing scaling and corrosion caused by metal ions.
- Food Preservation: EDTA extends the shelf life of certain food products by preventing spoilage and deterioration.
- Agricultural Productivity: In agriculture, EDTA aids in nutrient uptake by plants, leading to improved crop yields.
- Medicinal Applications: In medicine, EDTA is used to treat heavy metal poisoning and as a chelating agent in certain medical procedures.
How EDTA is Made
The production of EDTA typically involves the following steps:
- Raw Materials: The primary raw materials used in EDTA production include ethylenediamine, formaldehyde, and sodium cyanide.
- Synthesis: These raw materials undergo a series of chemical reactions to produce EDTA.
- Purification: The resulting mixture is purified to remove impurities and unwanted byproducts.
- Formulation: The purified EDTA is formulated into various product forms, such as liquid solutions or solid powders, depending on its intended application.
In conclusion, Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA) is a vital chemical compound with extensive applications in water treatment, detergents, food preservation, medicine, agriculture, and more. Its chelating properties make it effective in controlling and removing metal ions, which can have adverse effects in various processes. The versatility and benefits of EDTA underscore its importance in industries where the management of metal ions is essential for optimal performance and efficiency. Understanding its applications and production process highlights its significance in diverse industrial sectors.
Where can I buy EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) in Europe ?
Contact us for EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid) availability and prices