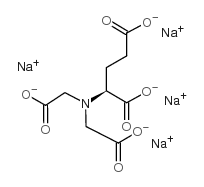
GLDA (Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate)
What is GLDA?
GLDA, or Tetrasodium glutamate diacetate, is a biodegradable chelating agent used in various industries for its exceptional ability to bind to metal ions. This versatile compound is a derivative of glutamic acid, an amino acid found in living organisms. GLDA is highly water-soluble and environmentally friendly, making it a preferred choice for applications where chelation and metal ion control are essential.
Applications of GLDA
- Cleaning Products: GLDA is a key ingredient in many household and industrial cleaning products. It helps remove mineral deposits and prevents scale buildup in dishwashers, washing machines, and industrial equipment.
- Personal Care Products: In personal care items such as shampoos, soaps, and shower gels, GLDA is used to improve the stability and effectiveness of these products.
- Food and Beverage Industry: GLDA is utilized as a food additive in the food industry. It helps preserve the color, flavor, and quality of various processed foods by chelating metal ions that can cause spoilage or degradation.
- Agriculture: GLDA can be used in agriculture as a chelating agent for soil amendments, ensuring that essential nutrients are available to plants while minimizing nutrient loss due to soil pH or metal ion interactions.
GLDA: Benefits
The utility of Glutamic Acid Diacetate can be attributed to several key advantages:
- Biodegradability: GLDA is biodegradable, which means it breaks down naturally in the environment, posing minimal harm to ecosystems.
- High Chelation Efficiency: It has a high affinity for metal ions, making it effective in preventing metal-related issues such as scale formation and discoloration.
- Environmentally Friendly: Its biodegradability and low toxicity make it an environmentally friendly option for various applications.
- Compatibility: GLDA is compatible with a wide range of other ingredients, making it a versatile choice for formulation in various products.
How GLDA is Made
The production of GLDA involves several chemical steps:
- Glutamic Acid: Glutamic acid, an amino acid derived from vegetable sources like sugar beets or wheat, serves as the starting material.
- Esterification: Glutamic acid undergoes esterification to produce a compound known as glutamic acid diethyl ester.
- Hydrolysis: Hydrolysis of the ester yields the final product, Glutamic Acid Diacetic Acid or GLDA.
The resulting GLDA is then purified and formulated into the desired products or applications.
In conclusion, Glutamic Acid Diacetate (GLDA) is a versatile chelating agent used in various industries due to its ability to bind to metal ions and prevent issues such as scaling and spoilage. Its biodegradability, compatibility, and environmentally friendly nature make it a valuable ingredient in cleaning products, personal care items, and the food and beverage industry. Understanding its benefits and production process underscores its significance in modern manufacturing and product development.
Where can I buy GLDA (Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate) in Europe ?
Contact us for GLDA (Tetrasodium Glutamate Diacetate) availability and prices