Silanes
What are Silanes?
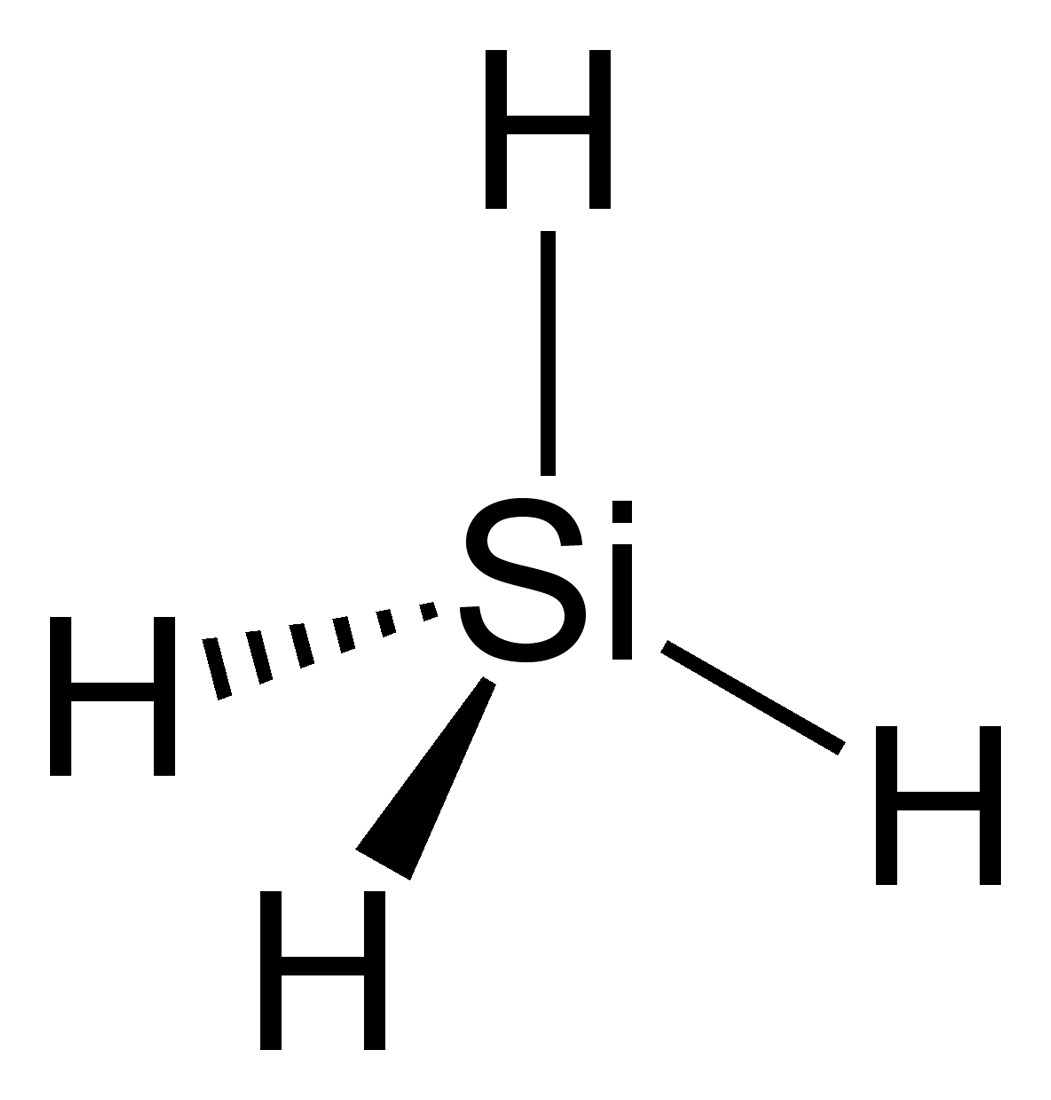
Silanes are a group of chemical compounds composed of silicon (Si) and hydrogen (H) atoms, along with other organic groups such as methyl (CH3) or ethyl (C2H5) groups. They are known for their unique properties and wide range of applications across various industries. Silanes play a crucial role in the field of materials science and are particularly valued for their ability to bond with both organic and inorganic materials, making them versatile coupling agents and surface modifiers.
Applications of Silanes
- Adhesives and Sealants: Silanes are commonly used as adhesion promoters in the formulation of adhesives and sealants. They improve the bonding strength between dissimilar materials, such as glass to metal or rubber to metal.
- Construction Materials: Silanes are used in the construction industry as water repellents and surface protectants for concrete and masonry. They enhance the durability of structures by reducing water penetration and corrosion.
- Plastics and Polymers: Silanes are employed as coupling agents in the production of reinforced plastics and rubber. They improve the adhesion between the polymer matrix and reinforcing materials like glass fibers or minerals.
- Paints and Coatings: In the formulation of paints and coatings, silanes are used as crosslinkers, adhesion promoters, and corrosion inhibitors. They enhance the adhesion of coatings to various substrates and improve their resistance to environmental factors.
- Electronic Devices: Silanes are utilized in the electronics industry as dielectric materials, passivation layers, and adhesion promoters in semiconductor devices and integrated circuits.
- Pharmaceuticals: Silanes are employed in pharmaceutical research and development for the modification of drug delivery systems, surface modification of medical devices, and as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceutical compounds.
Silanes: Benefits
The use of silanes offers several key benefits:
- Adhesion Enhancement: Silanes are highly effective adhesion promoters, facilitating strong bonds between dissimilar materials.
- Water Repellency: Silanes can impart water-repellent properties to surfaces, reducing the penetration of moisture and enhancing durability.
- Corrosion Resistance: In coatings and sealants, silanes improve resistance to corrosion, extending the lifespan of materials and structures.
- Versatility: Silanes can be tailored to specific applications by modifying their organic groups, making them versatile in various industries.
How Silanes are Made
The production of silanes involves several key steps:
- Silicon Source: Silicon is extracted from minerals like quartz, sand, or clay, and then converted into silicon tetrachloride (SiCl4).
- Hydrosilation: Silanes are typically synthesized through a hydrosilation reaction, where silicon tetrachloride reacts with hydrogen gas (H2) or a suitable organic compound containing Si-H bonds. This reaction produces various types of silanes with different organic groups.
- Purification: The crude silanes are purified to remove impurities and unreacted materials. Distillation and other purification methods may be employed.
- Formulation: The purified silanes can be formulated into different products, such as liquid silane coupling agents or silane-modified polymers, depending on their intended applications.
In conclusion, silanes are essential chemical compounds with a wide range of applications in adhesives, construction materials, plastics, coatings, electronics, and pharmaceuticals. Their ability to enhance adhesion, provide water repellency, and resist corrosion makes them valuable in multiple industries. Understanding their applications and production process highlights their significance in improving the performance and functionality of various products and materials.
Where can I buy Silanes in Europe ?
Contact us for Silanes availability and prices