Acrylates
What are Acrylates?
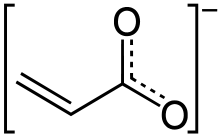
Acrylates are a group of chemical compounds that contain the acrylate functional group, characterized by a carbon double bond (C=C) and a carbonyl group (C=O). These compounds are derivatives of acrylic acid and are known for their versatility and wide range of applications across various industries. Acrylates can exist in various forms, including liquid monomers and solid polymers.
Applications of Acrylates
- Adhesives and Sealants: Acrylate-based adhesives are used in a wide range of applications, including packaging, construction, and automotive assembly. They provide strong bonding capabilities and resistance to environmental factors.
- Paints and Coatings: Acrylate polymers are essential components in paints and coatings. They contribute to the film-forming properties, adhesion, and durability of coatings used in architectural, automotive, and industrial applications.
- Textiles: Acrylate-based polymers are used in textiles to improve fabric properties such as wrinkle resistance, water repellency, and flame resistance. They are commonly applied as coatings or finishes on fabrics.
- Medical Devices: Acrylates are used in the production of medical devices, including contact lenses, wound dressings, and dental materials. Their biocompatibility and optical clarity make them suitable for these applications.
- Personal Care Products: Acrylates are found in various personal care products, including hair gels, nail polishes, and skin care formulations. They provide texture, hold, and film-forming properties.
Acrylates: Benefits
The use of acrylates offers several key benefits:
- Adhesion: Acrylates provide strong adhesion to a wide range of substrates, making them valuable in adhesive and coating applications.
- Flexibility: Acrylate-based materials are known for their flexibility and resilience, making them suitable for applications where material flexibility is required.
- Quick Curing: Many acrylate formulations cure rapidly when exposed to UV light or heat, reducing processing time in various applications.
- Chemical Resistance: Acrylates often exhibit resistance to chemicals and environmental factors, contributing to the durability of coatings and adhesives.
How Acrylates are Made
The production of acrylates involves several key steps:
- Raw Materials: The primary raw material for acrylate production is acrylic acid, which can be derived from propylene or ethylene through a series of chemical processes.
- Polymerization: Acrylic acid is polymerized to form various acrylate monomers, depending on the desired end product. This process can be initiated through heat, light, or chemical initiators.
- Purification: The resulting acrylate monomers are purified to remove impurities and unreacted materials.
- Formulation: The purified monomers are then formulated into liquid or solid forms, depending on their intended applications. In some cases, additional additives or cross-linking agents may be incorporated.
In conclusion, acrylates are a versatile group of compounds with a wide range of applications, including adhesives, coatings, textiles, medical devices, and personal care products. Their adhesion, flexibility, and rapid curing properties make them valuable in numerous industrial sectors. Understanding their applications and production process underscores their significance in enhancing the functionality and performance of various products.
Where can I buy Acrylates in Europe ?
Contact us for Acrylates availability and prices